https://prinha.tistory.com/entry/JAVA%EC%9E%90%EB%A3%8C%EA%B5%AC%EC%A1%B0-Stack-Interface
[JAVA/자료구조] Stack Interface
Stack 후입선출(LIFO) 한 번쯤, StackOverflowError를 마주할 수 있는데 재귀가 깊어지면서 발생한 오류이다. 메소드를 호출할 때마다 메소드 내에 정의된 변수들의 값이 Stack내에 쌓이게 되는데, 재귀가
prinha.tistory.com
Stack Interface Source
package Interface_form;
/**
*
* 자바 stack Interface입니다. <br>
* StackInterface는 Stack에 의해 구현됩니다.
*
* @author st_lab
* @param <E> the type of elements in this Stack
*
* @version 1.0
*
*/
public interface StackInterface<E> {
/**
* 스택의 맨 위에 요소를 추가합니다.
*
* @param item 스택에 추가할 요소
* @return 스택에 추가된 요소
*/
E push(E item);
/**
* 스택의 맨 위에 있는 요소를 제거하고 제거 된 요소를 반환합니다.
*
* @return 제거 된 요소
*/
E pop();
/**
* 스택의 맨 위에 있는 요소를 제거하지 않고 반환합니다.
*
* @return 스택의 맨 위에 있는 요소
*/
E peek();
/**
* 스택의 상반 부터 특정 요소가 몇 번째 위치에 있는지를 반환합니다.
* 중복되는 원소가 있을경우 가장 위에 있는 요소의 위치가 반환됩니다.
*
* @param value 스택에서 위치를 찾을 요소
* @return 스택의 상단부터 처음으로 요소와 일치하는 위치를 반환.
* 만약 일치하는 요소가 없을 경우 -1 을 반환
*/
/*
* ________
* | a |
* idx 3 |______| search("w")
* | e | --> 상단(idx 3)으로 부터 3번 째에 위치
* idx 2 |______| == return 되는 값 : 3
* | w |
* idx 1 |______|
* | k |
* idx 0 |______|
*
*/
int search(Object value);
/**
* 스택의 요소 개수를 반환합니다.
*
* @return 스택에 있는 요소 개수를 반환
*/
int size();
/**
* 스택에 있는 모든 요소를 삭제합니다.
*/
void clear();
/**
* 스택에 요소가 비어있는지를 반환합니다.
*
* @return 스택에 요소가 없을 경우 {@code true}, 그 외의 경우 {@code false}를 반환
*/
boolean empty();
}
Stack
Object[] 배열을 사용하는 스택
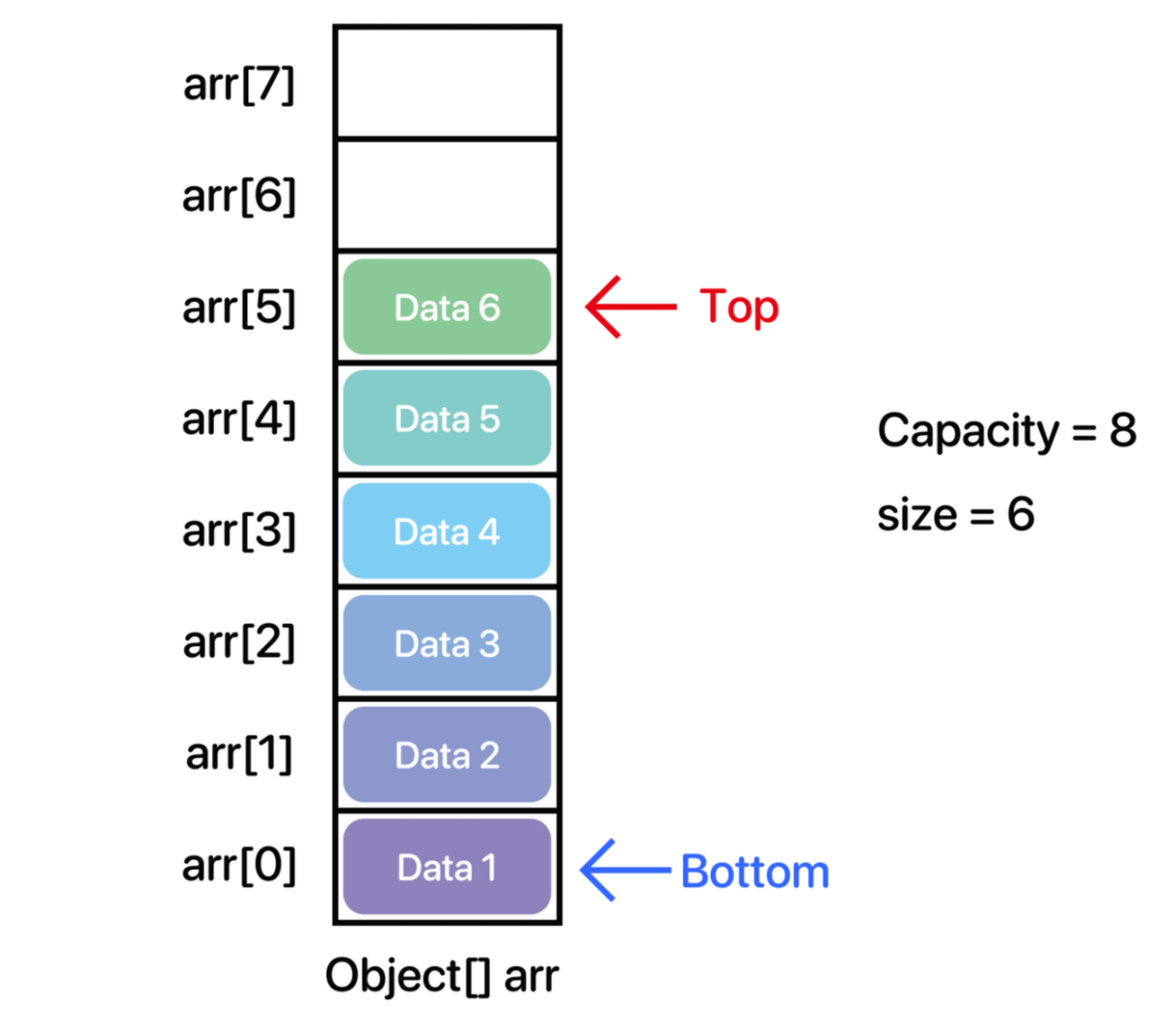
Bottom : 가장 밑에 있는 데이터 또는 그 데이터의 인덱스
Top : 가장 위에 있는 데이터 또는 그 데이터의 인덱스
Capacity : 데이터를 담기 위한 용적
Size: 데이의 개수
0. Stack 클래스 및 생성자 구성
import Interface_form.StackInterface;
public class Stack<E> implements StackInterface<E> {
// 상수로 쓸 것이기때문에 static final 키워드 붙여주기
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; // 최소(기본) 용적 크기
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ARRAY = {}; // 빈 배열
private Object[] array; // 요소를 담을 배열
private int size; // 요소 개수
// 생성자1 (초기 공간 할당 X)
public Stack() {
this.array = EMPTY_ARRAY;
this.size = 0;
}
// 생성자2 (초기 공간 할당 O)
public Stack(int capacity) {
this.array = new Object[capacity];
this.size = 0;
}
}
1) 생성자1의 경우 사용자가 공간 할당을 미리 안하고 객체만 생성하고 싶을 때
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
2) 생성자2의 경우 사용자가 데이터의 개수를 예측하여 미리 공간을 할당하고 싶을 때
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(100);
1. 동적할당을 위한 resize 메소드
private void resize() {
// 빈 배열일 경우 (capacity is 0)
if(Arrays.equals(array, EMPTY_ARRAY)) {
array = new Object[DEFAULT_CAPACITY];
return;
}
int arrayCapacity = array.length; // 현재 용적 크기
// 용적이 가득 찰 경우
if(size == arrayCapacity) {
int newSize = arrayCapacity * 2;
// 배열 복사
array = Arrays.copyOf(array, newSize);
return;
}
// 용적의 절반 미만으로 요소가 차지하고 있을 경우
if(size < (arrayCapacity / 2)) {
int newCapacity = (arrayCapacity / 2);
// 배열 복사
array = Arrays.copyOf(array, Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, newCapacity));
return;
}
}
1) if(Arrays.equals(array, EMPTY_ARRAY)) - 빈 배열일 경우
별도로 용적을 설정하지않은 경우 최소 용적의 크기만큼 배열을 생성해준다.
2) if(size == arrayCapacity) - 용적이 가득 찰 경우
데이터가 꽉 찰 경우 용적을 현재 용적의 2배로 늘려주는 설정을 한다.
기존에 담겨있던 요소들을 새롭게 복사해야 하는데, 이 때 편리하게 쓸 수 있는 것이 Arrays.copyOf 메소드이다.
3) if(size < (arrayCapacity / 2)) - 용적의 절반 미만으로 요소가 차지하고 있을 경우
데이터가 용적의 절반 미만을 차지하고 있을 경우 용적도 절반으로 줄여주는 메소드이다.
DEFAULT_CAPACITY보다 아래로 떨어지지않게 비교하여 사용한다.
2. push
@Override
public E push(E item) {
// 용적이 꽉 차있다면 용적을 재할당 해준다.
if (size == array.length) {
resize();
}
array[size] = item; // 마지막 위치에 요소 추가
size++; // 사이즈 1 증가
return item;
}
3. pop
@Override
public E pop() {
// 만약 삭제할 요소가 없다면 Stack이 비어있다는 의미이므로 예외 발생시키기
if(size == 0) {
throw new EmptyStackException();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E obj = (E) array[size - 1]; // 삭제될 요소를 반환하기 위한 임시 변수
array[size - 1] = null; // 요소 삭제
size--; // 사이즈 1 감소
resize(); // 용적 재할당
return obj;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
해당 어노테이션을 붙이지않으면 type safe(타입 안정성)에 대해 경고를 보낸다.
반환되는 것을 보면 E타입으로 캐스팅을 하고 있고 그 대상이 되는 것은 Object배열의 Object데이터이다.
Object -> E 타입으로 변환을 하는 것인데 이 과정에서 변환할 수 없는 타입이 있을 가능성이 있어 경고가 뜨는데, 우리가 push하여 받아들이는 데이터 타입은 유일하게 E타입만 존재해서 형 안정성이 보장된다.
한마디로 ClassCastException을 무시하겠다는 말인데, 절대 남발해서는 안되며 형 변환시 예외 가능성이 전혀 없을 경우에만 쓰는 것이 좋다.
4. peek
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public E peek() {
// 만약 삭제할 요소가 없다면 Stack이 비어있다는 의미이므로 예외 발생시키기
if(size == 0) {
throw new EmptyStackException();
}
return (E) array[size - 1];
}
5. search
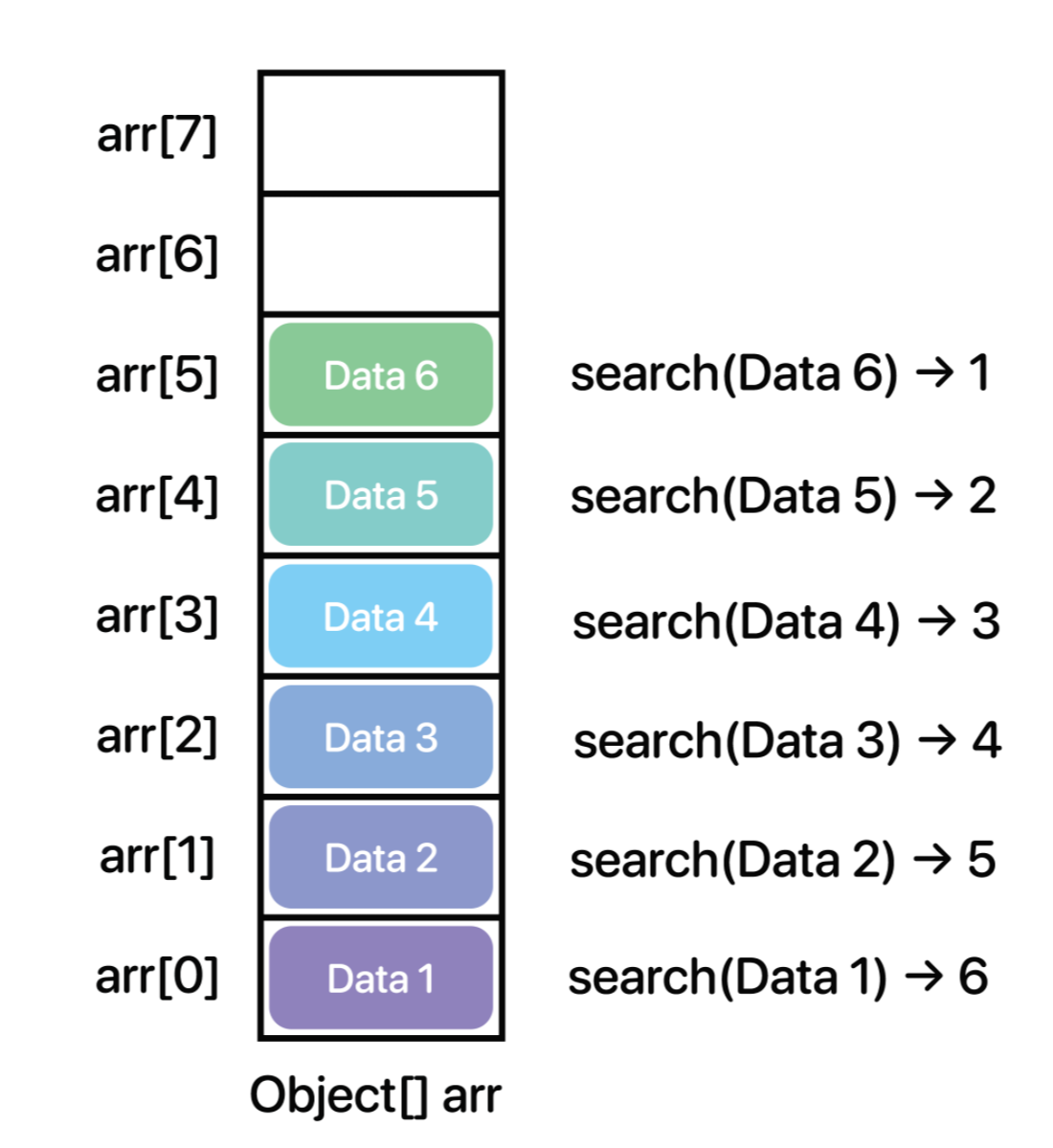
찾으려는 데이터가 상단의 데이터로부터 얼마만큼 떨어져 있는지에 대한 상대적 위치 값
@Override
public int search(Object value) {
for(int idx = size - 1; idx >= 0; idx--) {
// 같은 객체를 찾았을 경우 size - idx 값을 반환
if(array[idx].equals(value)) {
return size - idx;
}
}
return -1;
}
6. size
@Override
public int size() {
return size;
}
7. clear
모든 배열을 명시적으로 null처리, size=0
@Override
public void clear() {
// 저장되어있던 모든 요소를 null 처리 해준다.
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
array[i] = null;
}
size = 0;
resize();
}
8. empty
stack이 비어있는지 확인하는 메소드
@Override
public boolean empty() {
return size == 0;
}
9. clone
@Override
public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
// 새로운 스택 객체 생성
Stack<?> cloneStack = (Stack<?>) super.clone();
// 새로운 스택의 배열도 생성해주어야 함(내부 객체는 깊은 복사가 되지 않기 때문)
cloneStack.array = new Object[size];
// 현재 배열을 새로운 스택의 배열에 값을 복사함
System.arraycopy(array, 0, cloneStack.array, 0, size);
return cloneStack;
}Stack<Integer> original = new Stack<>();
original.push(10); // original에 10추가
Stack<Integer> copy = original;
Stack<Integer> clone = (Stack<Integer>) original.clone();
copy.push(20); // copy에 20추가
clone.push(30); // clone에 30추가
System.out.println("original Stack");
int i = 0;
for(Object a : original.toArray()) {
System.out.println("index " + i + " data = " + a);
i++;
}
System.out.println("\ncopy Stack");
i = 0;
for(Object a : copy.toArray()) {
System.out.println("index " + i + " data = " + a);
i++;
}
System.out.println("\nclone Stack");
i = 0;
for(Object a : clone.toArray()) {
System.out.println("index " + i + " data = " + a);
i++;
}
System.out.println("\noriginal stack reference : " + original);
System.out.println("copy stack reference : " + copy);
System.out.println("clone stack reference : " + clone);
깊은 복사를 위해 필요한 것이 clone()메소드 인데, Object에 있는 메소드지만 접근제어자가 protected로 되어있어
이를 구현해야 할 경우 반드시 Cloneable 인터페이스를 implement 해야한다.
즉, public class Stack<E> implements StackInterface<E>에 Cloneable도 추가해주어야 한다.
10. toArray
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
// get Stack to array (using toArray())
Object[] Stack1 = stack.toArray();
// get Stack to array (using toArray(T[] a)
Integer[] Stack2 = new Integer[10];
stack2 = stack.toArray(Stack2);public Object[] toArray() {
return Arrays.copyOf(array, size);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
if (a.length < size)
return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(array, size, a.getClass());
System.arraycopy(array, 0, a, 0, size);
return a;
}
1) Object[] toArray()
아무런 인자 없이 현재 있는 Stack의 리스트를 객체배열(Object[])로 반환해주는 메소드
Stack에 있는 요소의 수만큼 정확하게 배열의 크기가 할당되어 반환된다.
2) T[] toArray(T[] a)
Stack을 이미 생성된 다른 배열에 복사해주고자 할 때 쓰는 메소드
객체 클래스로 상속관계에 있는 타입이거나 Wrapper(Integer -> int)같이 데이터 타입을 유연하게 캐스팅할 수 있는 여지가 있다.
stack1에 원소 5개가 있고, stack2 배열에 10개의 원소가 있다면 stack2에 0-4 index에 원소가 복사되고, 그 외의 원소는 기존 stack2배열에 초기화 되어있던 원소가 그대로 남는다.
11. sort
int[][] arr = new int[10][10];
Arrays.sort(arr, new Comparator<int[]>() {
@Override
public int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2) {
// 구현부
}
});
(c == null) 조건을 보면 Comparator인자가 있는지, 없는지를 말해주는데
인자가 없는 경우 해당 객체의 Comparable 구현이 있는지를 확인하고 있으면 정렬하고, 아니면 에러를 뱉는다.
sort()메소드를 구현할 때 Comparable이 구현되어 있어 따로 Comparator을 넘겨주지않는 경우와
Comparator을 넘겨주어 정의된 정렬 방식을 사용하는 경우 두 가지를 생각해야 한다.
public void sort() {
/**
* Comparator를 넘겨주지 않는 경우 해당 객체의 Comparable에 구현된
* 정렬 방식을 사용한다.
* 만약 구현되어있지 않으면 cannot be cast to class java.lang.Comparable
* 에러가 발생한다.
* 만약 구현되어있을 경우 null로 파라미터를 넘기면
* Arrays.sort()가 객체의 compareTo 메소드에 정의된 방식대로 정렬한다.
*/
sort(null);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {
Arrays.sort((E[]) array, 0, size, c);
}
Comparator<? super E>는 상속관계이면서 부모 클래스에서 정렬 방식을 따르는 경우도 생각하여 구현하였다.
이러한 경우를 고려하지 않는다면(종속관계에 영향을 안받는 객체) Comparator<E>로 해주어도 괜찮다.
1) Comparable
해당 객체의 기본 정렬 방법을 설정할 때
package _04_Stack;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Student> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(new Student("김자바", 92));
stack.push(new Student("이시플", 72));
stack.push(new Student("조시샵", 98));
stack.push(new Student("파이손", 51));
stack.sort(); // Comparator 인자가 필요하지 않음
for(Object a : stack.toArray()) {
System.out.println(a);
}
}
}
class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
String name;
int score;
Student(String name, int score){
this.name = name;
this.score = score;
}
public String toString() {
return "이름 : " + name + "\t성적 : " + score;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
return o.score - this.score;
}
}
2) Comparator
특정한 경우에 임시적으로 쓸 수 있게 정렬을 정의할 때 (사용자 정의 클래스의 경우 필수)
package _04_Stack;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Student> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(new Student("김자바", 92));
stack.push(new Student("이시플", 72));
stack.push(new Student("조시샵", 98));
stack.push(new Student("파이손", 51));
stack.sort(customComp); // Comparator을 넘겨준다.
for(Object a : stack.toArray()) {
System.out.println(a);
}
}
// 사용자 설정 comparator(비교기)
static Comparator<Student> customComp = new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o2.score - o1.score;
}
};
}
class Student {
String name;
int score;
Student(String name, int score){
this.name = name;
this.score = score;
}
public String toString() {
return "이름 : " + name + "\t성적 : " + score;
}
}
Stack은 Vector를 상속받고, Vector는 ArrayList와 구조가 유사하다.
ArrayList를 상속받아 쓸 수 있다.
import java.util.EmptyStackException;
import Interface_form.StackInterface;
import _01_ArrayList.ArrayList;
/**
*
* @author (st-lab.tistory.com)
*
* @param <E> the type of elements in this stack
*/
public class StackExtendArrayList<E> extends ArrayList<E> implements StackInterface<E> {
// 초기 용적 할당 X
public StackExtendArrayList() {
super();
}
// 초기 용적 할당 O
public StackExtendArrayList(int capacity) {
super(capacity);
}
@Override
public E push(E item) {
addLast(item); // ArrayList의 addLast()
return item;
}
@Override
public E pop() {
int length = size();
E obj = remove(length - 1); // ArrayList의 remove()
return obj;
}
@Override
public E peek() {
int length = size();
if (length == 0)
throw new EmptyStackException();
E obj = get(length - 1); // ArrayList의 get()
return obj;
}
@Override
public int search(Object value) {
int idx = lastIndexOf(value); // ArrayList의 lastIndexOf()
if(idx >= 0) {
return size() - idx;
}
return -1;
}
@Override
public boolean empty() {
return size() == 0;
}
}
출처 및 참고
https://st-lab.tistory.com/174
[JAVA/자료구조] 자바 컬렉션 프레임워크(java collection framework) 총정리
- 컬렉션(collection) : 여러 객체(데이터)를 담을 수 있는 자료구조, 다수의 데이터 그룹 - 프레임워크(framework) : 표준화, 정형화된 체계적인 프로그래밍 방식 ▶ 컬렉션 프레임워크(collection framework)
prinha.tistory.com
'Programming > Algorithm&DataStructure' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JAVA/자료구조] Queue Interface (0) | 2021.08.19 |
|---|---|
| [JAVA/자료구조] Stack Interface (0) | 2021.08.09 |
| [JAVA 자료구조] Doubly LinkedList (이중 연결리스트) (0) | 2021.08.09 |
| [JAVA 자료구조] Singly LinkedList (단일 연결리스트) (0) | 2021.08.05 |
| [JAVA 자료구조] ArrayList (0) | 2021.08.04 |



